Oct 10, 2024
In the maritime industry, profitability is critical. Whether you’re managing a single vessel or a large fleet, one of the key tools to assess financial performance is the Voyage P&L, also known as Voyage Profit and Loss. This financial statement helps shipping companies break down voyage costs and revenues, providing insights into the profitability of specific voyages. Proper management of Voyage P&L and your overall Voyage Accounting allows operators and owners to make informed decisions, optimizing profitability while controlling costs.
In this blog, we’ll explore the key components of Voyage P&L, its importance in the shipping industry, and how it differs in the context of Voyage Chartering and Time Chartering. We’ll also discuss how a Voyage Management System, like ClearVoyage, can streamline the process, ensuring optimal financial performance.

What is Voyage P&L?
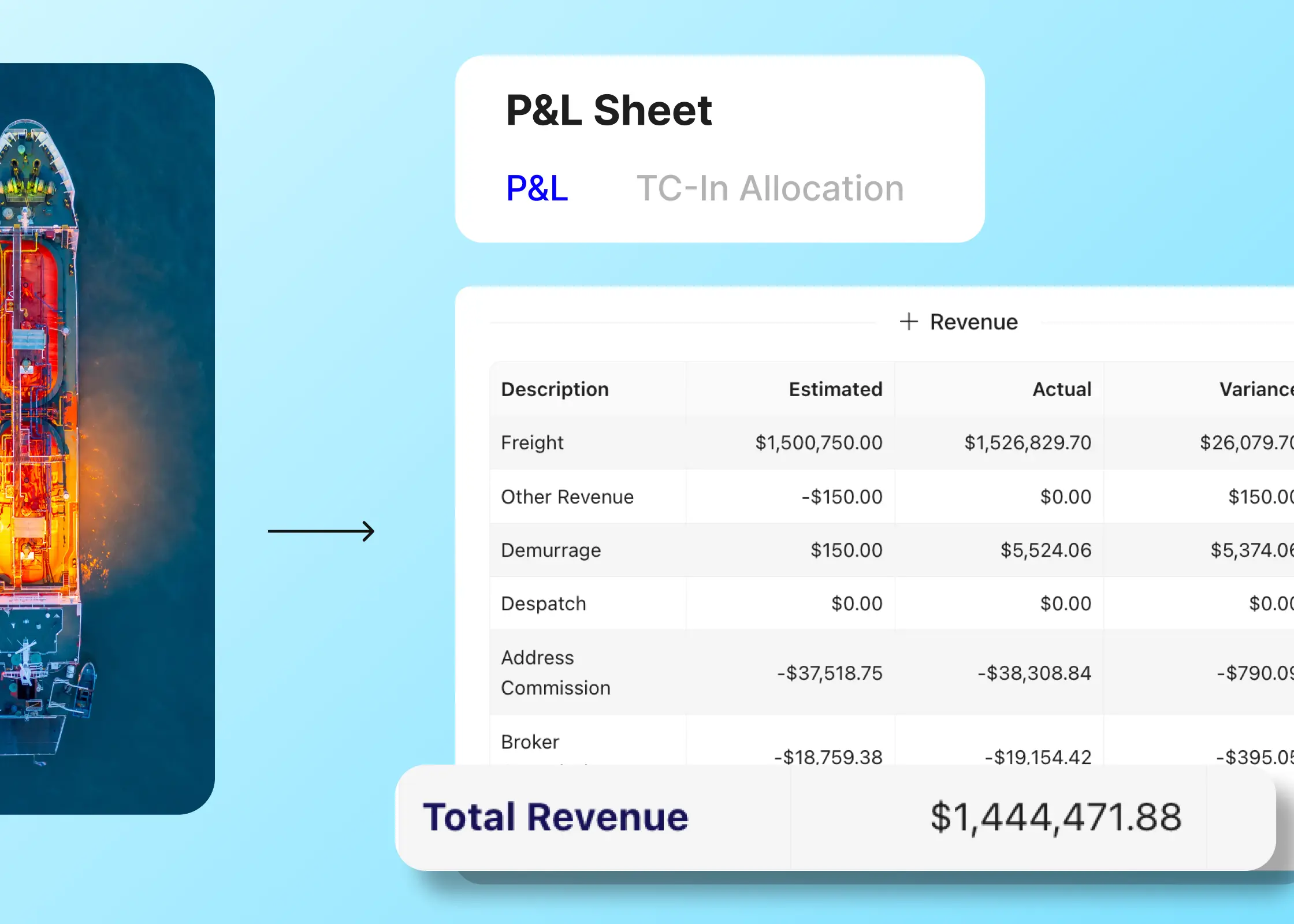
A Voyage P&L is a financial report that summarizes the total revenue generated from a voyage against all costs associated with it. It includes detailed line items for expenses such as fuel, port charges, crew wages, and any other operational costs. The main goal of a Voyage P&L is to determine whether a specific voyage was profitable or not, and to identify areas where expenses can be controlled or revenues enhanced in future operations.
In a highly competitive industry like shipping, having a clear understanding of voyage profitability is essential. Fluctuations in fuel prices, port fees, and market rates for cargo can dramatically affect the outcome of a voyage, making the Voyage P&L a crucial decision-making tool for operators.
Key Components of Voyage P&L
Revenue: The total income generated from transporting cargo, typically based on freight rates for voyage charters or hire rates for time charters. It can also include demurrage fees (penalties charged to charterers for delays in loading/unloading).
Bunker Costs: Bunker fuel is one of the largest expenses in any voyage. This includes the cost of purchasing fuel and any related expenses such as bunkering fees or taxes.
Port Charges: Fees incurred at ports during loading and unloading. These include docking fees, pilotage, tugs, and customs charges.
Canal Fees: For voyages that pass through canals like the Suez or Panama, specific fees apply. These can be substantial, particularly for larger vessels.
Crew and Manning Costs: Includes salaries, provisions, insurance, and other costs related to crew members during the voyage.
Other Operating Costs: This category covers any additional expenses, such as maintenance, spare parts, insurance premiums, and any unforeseen costs that arise during the voyage.
Freight Commission: For voyage charters, commissions paid to brokers or agents for securing cargo are included in the Voyage P&L.
Laytime and Demurrage: Laytime is the amount of time allocated for cargo operations (loading and unloading). If the charterer exceeds this time, demurrage penalties may be applied, which adds to revenue for the shipowner.
Profit/Loss Calculation: After summing all revenues and subtracting the total voyage costs, the result is the net profit or loss for that specific voyage.
Why is Voyage P&L Important?
Voyage P&L provides critical insights into the financial viability of each voyage. It helps shipping companies:
Identify profitable routes: By analyzing which voyages consistently generate profits, operators can plan future routes more strategically.
Control costs: A detailed breakdown of expenses highlights where costs can be reduced or optimized.
Compare performance: Shipping companies can use Voyage P&L reports to compare different voyages and charters, identifying patterns that lead to higher profitability.
Support decision-making: A comprehensive P&L statement informs both short-term decisions (such as route optimization) and long-term strategies (such as fleet expansion).
Voyage P&L in Voyage Chartering vs. Time Chartering
Voyage Chartering and Time Chartering are two main types of contracts in shipping, and they affect how the Voyage P&L is structured.
Voyage Chartering
In Voyage Chartering, the shipowner agrees to transport specific cargo for a single voyage between designated ports. The revenue is based on a fixed freight rate, and the shipowner is responsible for nearly all operational costs, including fuel, port charges, and canal fees. Because of this, the Voyage P&L for a voyage charter will have a more detailed breakdown of these costs.
In Voyage Chartering, laytime is an important factor. If the charterer delays the vessel at port beyond the allowed laytime, they incur demurrage charges, which add to the revenue side of the P&L. However, if the loading/unloading is completed early, the shipowner may have to pay despatch (a reward for early completion), which is an additional cost in the P&L.
Advantages of Voyage Chartering:
Predictable revenue: The freight rate is agreed upon before the voyage begins, making revenue predictable.
Less financial risk: The charterer has fewer financial risks, as they only commit to one specific voyage.
Disadvantages of Voyage Chartering:
Operational costs: The shipowner is responsible for all operational costs, which can fluctuate and affect profitability.
Single voyage focus: This charter type offers less flexibility in long-term planning, as it is based on individual voyages.
Time Chartering
In a Time Charter, the charterer hires the vessel for a set period, often several months or years. The charterer assumes responsibility for the vessel’s operating costs, such as fuel and port fees, but the shipowner still pays for the vessel’s maintenance, crew wages, and insurance.
The revenue in Time Chartering is based on a daily hire rate rather than a per-voyage freight rate, and the P&L for a time-chartered voyage typically includes more consistent income but fewer specific operational cost details.
For time charters, the Voyage P&L will track overall vessel utilization, helping to determine if the daily hire rate is sufficient to cover the operational costs and maintain profitability over the contract period.
Advantages of Time Chartering:
Steady revenue stream: A consistent daily hire rate allows for better revenue forecasting.
Operational control: The charterer can control the ship's routing and cargoes, providing flexibility for multiple voyages.
Disadvantages of Time Chartering:
Long-term commitment: The charterer is locked into a long-term contract, which may become costly if market conditions change.
Operational costs borne by the charterer: The charterer assumes fuel and port expenses, adding financial risk.
How a Voyage Management System Enhances Voyage P&L
Managing Voyage P&L manually can be a complex and time-consuming process, particularly when dealing with large fleets and numerous voyages. Shipping companies need to stay on top of fluctuating costs, track operational performance, and ensure compliance with financial regulations. This is where a Voyage Management System like ClearVoyage can provide immense value.
1. Automated P&L Tracking
ClearVoyage automates the process of calculating voyage expenses and revenues, ensuring accuracy and saving time. By pulling data from various operational areas such as bunker consumption, port charges, and route optimization, the system provides real-time updates on the financial health of each voyage.
2. Fuel and Port Cost Management
With volatile fuel prices and varying port charges, tracking these costs is critical for an accurate Voyage P&L. ClearVoyage’s integrated system enables precise fuel tracking and cost estimation for different ports, helping operators anticipate expenses and plan accordingly.
3. Real-Time Performance Monitoring
ClearVoyage offers real-time performance monitoring, allowing companies to track voyage progress and identify any deviations from the plan. This means that if a voyage incurs unexpected costs or underperforms, adjustments can be made quickly to minimize losses.
4. Laytime and Demurrage Calculations
Laytime and demurrage can significantly impact the financial outcome of a voyage. ClearVoyage simplifies laytime management by automatically calculating allowed laytime, tracking port operations, and generating demurrage or despatch reports. This ensures accurate invoicing and reduces disputes with charterers.
5. Comprehensive Reporting
With ClearVoyage, shipping companies gain access to detailed P&L reports, breaking down costs and revenues by voyage, vessel, or contract type. These insights help operators analyze performance across different time frames, enabling better strategic decisions and financial planning.
6. Seamless Integration with Accounting Systems
ClearVoyage seamlessly integrates with over 30 accounting systems, making it easier to reconcile financial data and track outstanding invoices. By automating invoicing and payment processes, companies can ensure timely cash flow and reduce administrative burdens.
Why ClearVoyage?
Managing voyage profitability can be challenging, but with ClearVoyage, shipping companies gain a powerful tool to monitor financial performance and optimize operations. By integrating chartering, operations, and accounting into a single platform, ClearVoyage provides complete visibility into the profitability of each voyage, helping companies stay competitive in the global shipping market.